Navigating the Complex Relationship Between Food and Heart Rhythm: Understanding QT Interval Prolongation
Navigating the Complex Relationship Between Food and Heart Rhythm: Understanding QT Interval Prolongation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex Relationship Between Food and Heart Rhythm: Understanding QT Interval Prolongation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content

Navigating the Complex Relationship Between Food and Heart Rhythm: Understanding QT Interval Prolongation
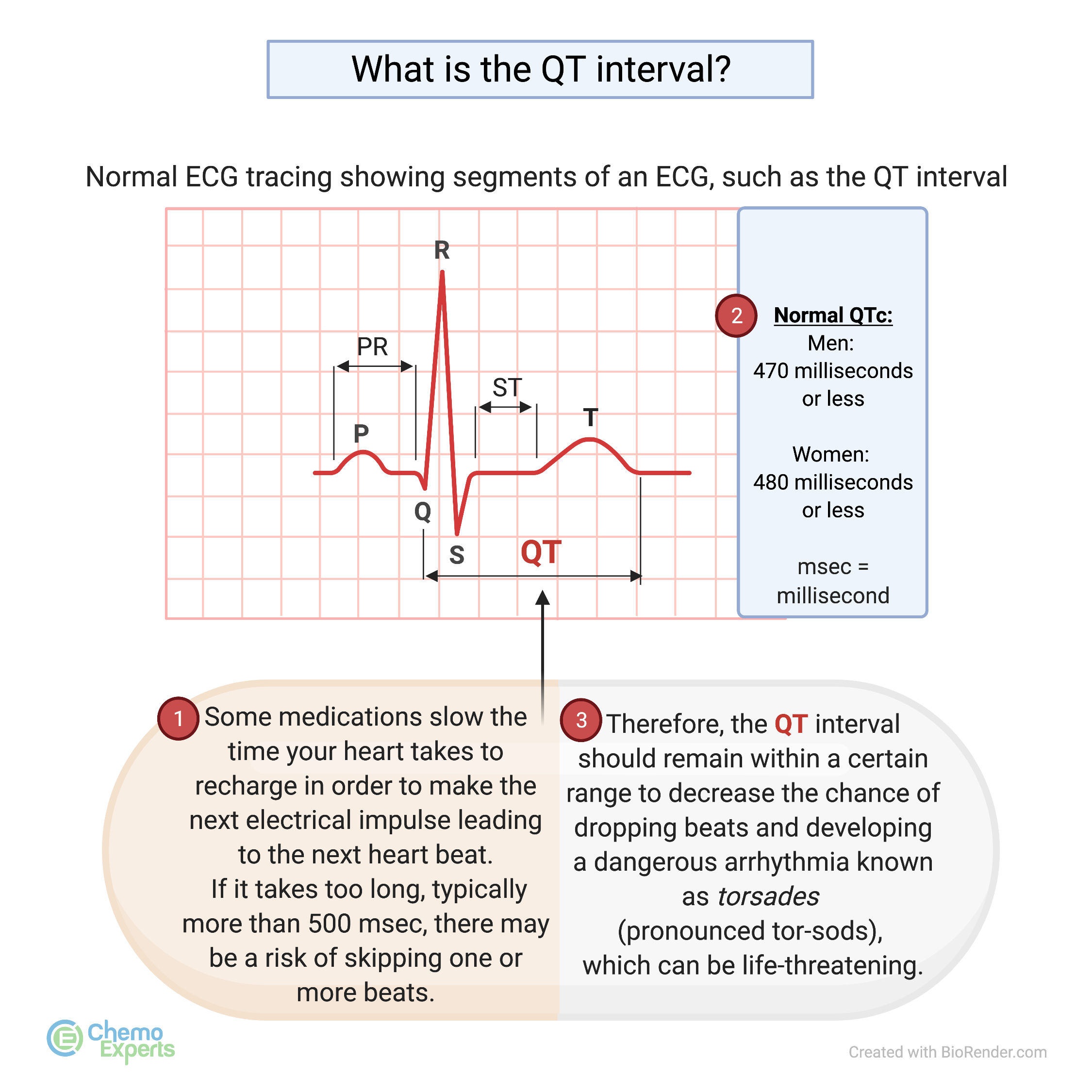
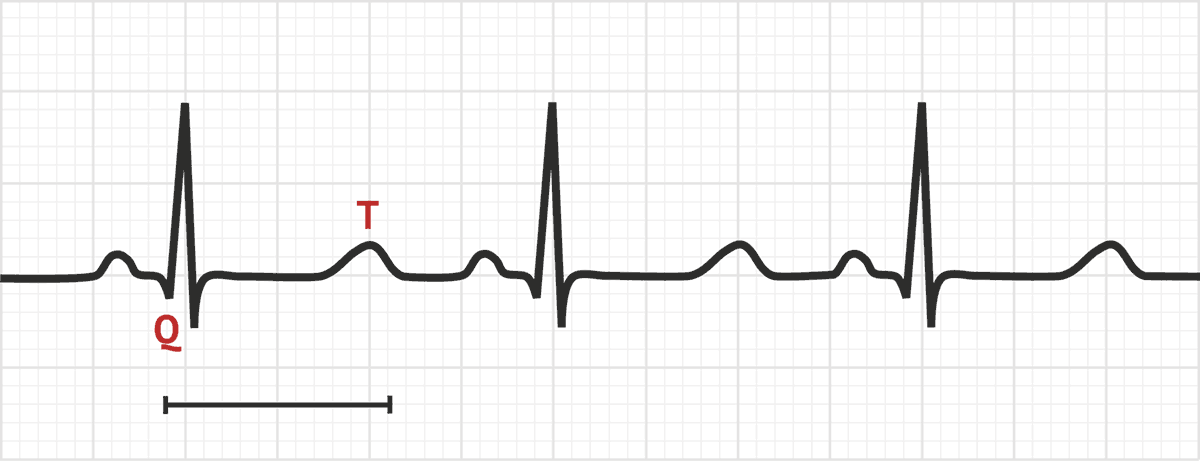
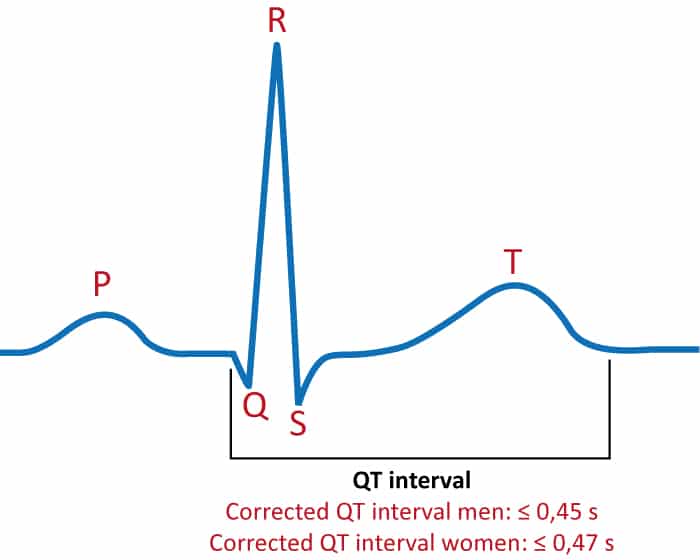
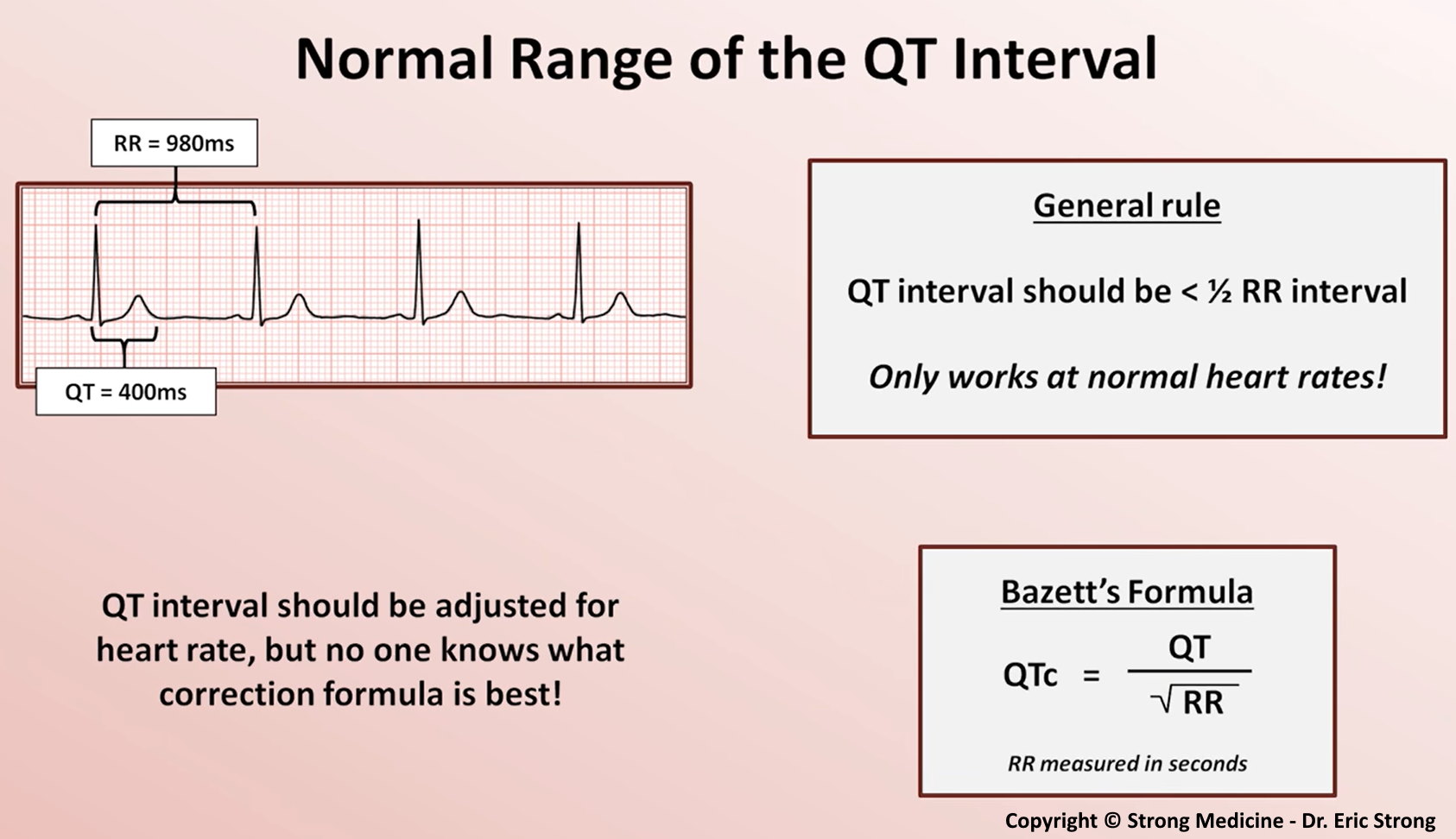
The human heart, a tireless pump, relies on a delicate interplay of electrical signals to maintain a steady rhythm. This rhythm is measured by an electrocardiogram (ECG), where the "QT interval" represents the time it takes for the ventricles, the heart’s lower chambers, to fully recharge after each heartbeat. A prolonged QT interval, indicating a delayed repolarization, can increase the risk of potentially life-threatening heart rhythm abnormalities, known as ventricular arrhythmias, including the dreaded torsades de pointes.
While genetics and certain medical conditions play a role in QT interval prolongation, dietary factors can also contribute to this phenomenon. Understanding these food-related influences is crucial for individuals at risk, as dietary modifications can potentially mitigate the risk of heart rhythm disturbances.
Foods that may contribute to QT interval prolongation:
1. Foods Rich in Potassium:
While potassium is essential for proper heart function, excessive intake can lead to a prolonged QT interval in susceptible individuals. This is particularly relevant for individuals with pre-existing conditions like hypokalemia (low potassium levels) or certain genetic predispositions.
Foods high in potassium include:
- Bananas: A common source of potassium, bananas are often recommended for their nutritional benefits. However, excessive consumption, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions, may contribute to QT prolongation.
- Avocados: These creamy fruits are rich in potassium and healthy fats. While beneficial in moderation, overconsumption might be problematic for some individuals.
- Potatoes: Baked, boiled, or mashed, potatoes provide a good source of potassium. However, moderation is key, especially for those at risk of QT prolongation.
- Tomatoes: These versatile fruits are a good source of potassium and lycopene. While generally healthy, excessive consumption should be avoided in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
- Beans and Lentils: These legumes are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and potassium. However, their potassium content warrants careful consideration for individuals with pre-existing conditions.
2. Foods Rich in Magnesium:
Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating heart rhythm. However, high magnesium levels, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions, can also contribute to QT interval prolongation.
Foods high in magnesium include:
- Dark Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are excellent sources of magnesium. While beneficial for overall health, moderation is crucial for individuals at risk of QT prolongation.
- Almonds: A popular snack, almonds are rich in magnesium, healthy fats, and fiber. However, excessive consumption should be avoided for individuals with pre-existing conditions.
- Avocados: These creamy fruits are rich in magnesium, potassium, and healthy fats. While beneficial in moderation, overconsumption might be problematic for some individuals.
- Black Beans: A versatile legume, black beans are a good source of magnesium, protein, and fiber. However, their magnesium content warrants careful consideration for individuals with pre-existing conditions.
3. Foods Containing High Levels of Certain Minerals:
- Licorice Root: This natural sweetener contains glycyrrhizic acid, which can cause hypokalemia and potentially prolong the QT interval. Excessive licorice consumption should be avoided.
- Black Tea: While black tea is generally considered safe, excessive consumption can lead to increased levels of manganese, which may contribute to QT prolongation in susceptible individuals.
4. Alcohol and Caffeine:
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt heart rhythm and prolong the QT interval. Moderation is key.
- Caffeine: High doses of caffeine can lead to an increased heart rate and potential QT interval prolongation. Individuals with pre-existing conditions should be particularly cautious.
5. Foods Containing Certain Compounds:
- Grapefruit: Grapefruit interacts with certain medications, including some used to treat heart conditions, potentially leading to QT interval prolongation. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional regarding potential interactions.
FAQs about Foods that Prolong QT Interval:
Q: Can I eat foods that prolong the QT interval if I have a pre-existing condition?
A: It’s crucial to consult with your healthcare professional about your specific condition and dietary recommendations. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual needs and risk factors.
Q: How much of a particular food is too much?
A: There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The amount of food that can contribute to QT prolongation varies from person to person and depends on individual factors like genetics, pre-existing conditions, and overall health status. It’s best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Q: Are there any foods that can help shorten the QT interval?
A: While specific foods cannot directly shorten the QT interval, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall heart health and potentially minimize the risk of QT prolongation.
Q: What are the symptoms of a prolonged QT interval?
A: In many cases, a prolonged QT interval doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms. However, in some individuals, it can lead to heart rhythm abnormalities like ventricular arrhythmias, potentially causing symptoms such as:
- Palpitations: A feeling of a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: Caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain.
- Fainting: Loss of consciousness due to a sudden drop in blood pressure.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: A life-threatening condition where the heart stops beating.
Tips for managing dietary factors related to QT interval prolongation:
- Consult a healthcare professional: Seek personalized advice from a doctor or registered dietitian to create a dietary plan that considers your individual needs and risk factors.
- Read food labels carefully: Pay attention to potassium, magnesium, and other mineral content in packaged foods.
- Choose a balanced diet: Focus on a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Moderation is key: Avoid excessive consumption of any food, especially those known to potentially contribute to QT prolongation.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration is crucial for overall heart health and can help regulate electrolyte balance.
Conclusion:
While a balanced diet plays a crucial role in overall heart health, certain foods can contribute to QT interval prolongation, potentially increasing the risk of heart rhythm disturbances. It’s essential to be aware of these dietary factors and consult with a healthcare professional to create a personalized dietary plan that minimizes risk. By understanding the potential impact of food on heart rhythm, individuals can make informed choices to support their heart health and well-being.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex Relationship Between Food and Heart Rhythm: Understanding QT Interval Prolongation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!